Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Do you ever feel like income tax is a puzzle you must solve every year? You’re not alone. Millions of taxpayers across India ask the same question: How do I calculate and pay the right amount of tax while making the most of available deductions?
The Details of the Income Tax Act 2025, as per Budget 202,5, bring several important updates for taxpayers. Whether you’re a salaried employee, a business owner, or self-employed, understanding the new rules helps you plan better and save smarter.
Think of income tax like a contribution jar everyone puts money into. The government then uses that jar to fund healthcare, education, roads, and public welfare. So, let’s break it down in simple language and walk through everything you need to know about Income Tax for FY 2025-26.
Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
| 1 | What is Income Tax? |
| 2 | Who Needs to Pay Income Tax in FY 2025-26? |
| 3 | Income Tax Slab Rates for Individuals |
| 4 | Income Tax Slabs for Businesses |
| 5 | Additional Surcharges and Cess |
| 6 | Types of Taxable Income |
| 7 | Filing Income Tax Returns (ITR) |
| 8 | Benefits of Filing ITR |
| 9 | Deductions Under Different Sections |
| 10 | Income Tax Rebate Explained |
| 11 | Difference Between Deduction and Exemption |
| 12 | Useful Tax Exemptions for Salaried Employees |
| 13 | How Income Tax on Salary is Calculated |
| 14 | Advance Tax: Who Should Pay It? |
| 15 | Smart Tax Planning Tips |
| 16 | Avoiding Tax Evasion |
| 17 | FAQs on Income Tax FY 2025-26 |
| 18 | Conclusion |
1. What is Income Tax?
Income tax is a direct tax that you pay on your income to the government. It applies to both individuals and businesses. The financial year runs from April 1 to March 31. The tax collected funds public services such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
2. Who Needs to Pay Income Tax in FY 2025-26?
You need to file and pay income tax if your annual taxable income exceeds ₹2.5 lakh (₹3 lakh for senior citizens and ₹5 lakh for very senior citizens). Taxpayers include:
- Salaried employees
- Self-employed professionals
- Businesses and corporate firms
- Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs)
- Local authorities and other legal entities
In short, if you earn, you file!
3. Income Tax Slab Rates for Individuals
Tax rates work progressively—meaning, the more you earn, the higher your tax percentage.
Old vs New Regime (FY 2025-26):
- Old Regime: Deductions allowed, but fewer slab benefits.
- New Regime: Simpler, with broader slabs but fewer deductions.
Example (New Regime, FY 2025-26):
- ₹0 – ₹4,00,000 → No tax
- ₹4,00,001 – ₹8,00,000 → 5%
- ₹8,00,001 – ₹12,00,000 → 10%
- ₹12,00,001 – ₹16,00,000 → 15%
- ₹16,00,001 – ₹20,00,000 → 20%
- ₹20,00,001 – ₹24,00,000 → 25%
- Above ₹24,00,000 → 30%
4. Income Tax Slabs for Businesses
- Domestic companies: 25% if turnover ≤ ₹400 crore, otherwise 30%.
- Special rates under sections 115BA, 115BAA, 115BAB: as low as 15%.
- Foreign companies: 40% on general income, 50% for certain royalties/technical services.
5. Additional Surcharges and Cess
- Surcharge: Extra tax on high incomes (10% to 37%).
- Health and Education Cess: 4% on the total tax.
6. Types of Taxable Income
- Salary Income
- Business/Professional Income
- Capital Gains (from property or shares)
- House Property Income
- Other Sources (lottery, dividends, etc.)
7. Filing Income Tax Returns (ITR)
You can file returns via the Income Tax e-filing portal.
- Mandatory if income > ₹2.5 lakh.
- Companies must file regardless of profit/loss.
- NRIs pay tax on Indian income.
8. Benefits of Filing ITR
Even if you’re not liable, filing has perks:
- Smooth loan approvals
- Easier visa processing
- Refunds on excess tax paid
- Proof of income for investments
9. Deductions Under Different Sections
Popular ones include:
- 80C: Up to ₹1.5 lakh (PF, ELSS, NSC, home loan principal).
- 80D: Health insurance premiums.
- 80E: Education loan interest.
- 80G: Donations to approved bodies.
10. Income Tax Rebate Explained
Under Section 87A, residents with taxable income up to ₹5 lakh get a rebate, reducing tax liability to zero.
11. Difference Between Deduction and Exemption
- Exemption: Specific income is completely tax-free.
- Deduction: Income is included first, then reduced by certain expenses/investments.
12. Useful Tax Exemptions for Salaried Employees
- House Rent Allowance (HRA)
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
- Leave encashment
- Voluntary Retirement Scheme (VRS) benefits
- Transport and education allowances
13. How Income Tax on Salary is Calculated
- Compute gross salary.
- Subtract deductions (HRA, 80C, etc.).
- Apply slab rates.
- Add cess/surcharge.
14. Advance Tax: Who Should Pay It?
If you expect to owe more than ₹10,000 in tax (self-employed, freelancers, NRIs), you must pay in instalments throughout the year.
15. Smart Tax Planning Tips
- Start early in the financial year.
- Invest in tax-saving instruments (ELSS, PPF, insurance).
- Consult a tax advisor if unsure.
- Keep records of all eligible expenses.
16. Avoiding Tax Evasion
Tax evasion = illegal, and penalties can be 3 times the concealed amount. Always file honestly to avoid fines and notices.
17. FAQs on Income Tax FY 2025-26
Q1. What is the maximum tax-free income under the new regime for FY 2025-26?
Under Budget 2025, no tax is payable up to ₹12.75 lakh for salaried individuals (including standard deduction).
Q2. Can women claim extra tax exemptions?
Currently, women do not get special exemptions.
Q3. What happens if I miss the filing deadline?
You can file a belated return by December 31, 2026, but with penalties.
Q4. How do I check my tax refund status?
Log into the income tax portal → “View Filed Returns” → Check refund status.
Q5. Is linking PAN with Aadhaar mandatory?
Yes, without linking, you cannot file an ITR.
18. Conclusion
The Details of the Income Tax Act 2025, as per Budget 2025, highlight a modern, progressive tax system aimed at simplifying compliance while boosting government revenue. By understanding slab rates, deductions, and filing requirements, you not only stay compliant but also save money wisely.
Remember: income tax is not just an obligation—it’s your contribution toward building a stronger India. So, stay informed, plan smart, and file on time!
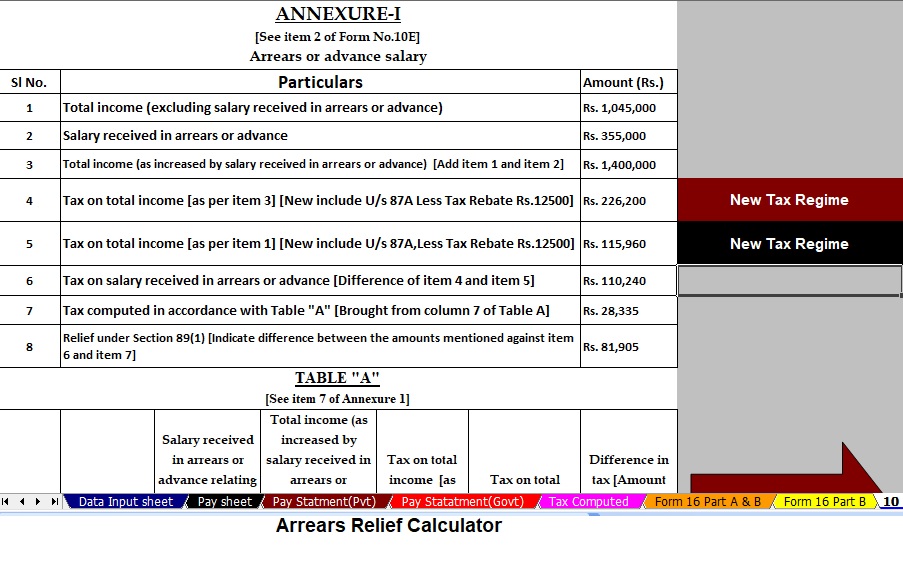
Download Automatic Income Tax Preparation Software in Excel for the Government and Non-Government Employees for the F.Y.2025-26 today.




Features of the Excel Utility
- User-Friendly Interface – The Excel Utility comes with a simple design that even beginners can use without technical knowledge.
- Automatic Tax Calculation – It calculates income tax instantly based on the latest financial year 2025-26 tax slabs.
- Both Old and New Regimes – The utility supports calculations under both regimes, helping users choose the most beneficial option.
- Pre-Loaded Deductions – It includes automatic deductions like standard deduction, HRA, Section 80C, 80D, and more.
- Custom Salary Structures – Government and non-government employees can input different salary formats easily.
- One-Click Comparison – Users can compare taxable income and tax payable under both regimes in seconds.
- HRA and Allowance Support – The tool auto-calculates House Rent Allowance and other allowances as per rules.
- Offline Access – Since it’s Excel-based, no internet connection is required once downloaded.
- Error-Free Computation – Built-in formulas reduce the risk of manual calculation mistakes.
- Printable Reports – Users can generate and print a ready-to-use tax statement for records or submission