Most of us keep a savings account, but here’s the catch—the interest you earn on it is taxable. Many people don’t realise that the seemingly small amounts of interest can add up and impact their income tax return. Under the Income Tax Act, this interest is considered “Income from Other Sources.”
Fortunately, Section 80TTA of the Income Tax Act comes to the rescue. It allows taxpayers to claim a deduction of up to ₹10,000 on the interest earned from savings bank accounts. This benefit is only available under the old tax regime.
To make things even easier, taxpayers can use an Automatic Income Tax Calculator in Excel with Form 10E, which simplifies everything from tax computation to arrears relief.
Let’s break down Section 80TTA in detail and see how you can save taxes smartly.
Table of Contents
ToggleTable of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
| 1 | What is Section 80TTA of the Income Tax Act? |
| 2 | Why was Section 80TTA introduced? |
| 3 | Key Features of Tax Savings Exemption U/s 80TTA |
| 4 | Eligibility for Claiming 80TTA Deduction |
| 5 | Income Eligible for 80TTA Deduction |
| 6 | Income Not Eligible under Section 80TTA |
| 7 | Difference Between Section 80TTA and Section 80TTB |
| 8 | How to Claim Section 80TTA Deduction in ITR |
| 9 | Step-by-Step Process to Report Savings Bank Interest |
| 10 | Benefits of Section 80TTA Deduction |
| 11 | Common Mistakes to Avoid While Claiming 80TTA |
| 12 | Old vs. New Tax Regime: Where Does 80TTA Fit? |
| 13 | Role of the Automatic Income Tax Calculator All-in-One |
| 14 | Features of the Excel Utility with Form 10E |
| 15 | Conclusion: Maximise Your Savings with 80TTA |
1. What is Section 80TTA of the Income Tax Act?
Section 80TTA is a provision that allows individual taxpayers and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) to claim a deduction on interest earned from savings accounts. You can reduce your taxable income by up to ₹10,000 per year under this section.
Think of it as a small tax shield that protects your hard-earned money from being taxed unnecessarily.
2. Why was Section 80TTA introduced?
The government introduced Section 80TTA to encourage small savings. Since savings accounts offer low interest rates compared to other instruments, this deduction ensures taxpayers still enjoy some relief on their modest earnings.
In a way, it acts like a reward for saving—you put money in your savings account, earn a little interest, and then reduce your tax burden.
3. Key Features of Tax Savings Exemption U/s 80TTA
- Deduction Limit: Up to ₹10,000.
- Source: Applies only to interest from savings accounts.
- Availability: For individuals and HUFs under the old regime.
- Not for NRIs: Non-Resident Indians cannot claim this benefit.
- Simple Claim: Easy to report in your ITR.
4. Eligibility for Claiming 80TTA Deduction
You are eligible if:
- You are an individual taxpayer or an HUF.
- Your savings account is with a bank, post office, or cooperative society.
- You file your return under the old tax regime.
There’s no upper age limit for this deduction—any individual can claim it.
5. Income Eligible for 80TTA Deduction
The following qualify for 80TTA benefits:
- Savings accounts in nationalised banks.
- Private banks’ savings accounts.
- Post office savings accounts.
- Cooperative societies’ savings accounts.
6. Income Not Eligible under Section 80TTA
The deduction does not apply to:
- Fixed Deposits (FDs).
- Recurring Deposits (RDs).
- Term Deposits.
- Interest from NBFCs.
- Interest from corporate bonds or debentures.
7. Difference Between Section 80TTA and Section 80TTB
- 80TTA: Available to all individuals and HUFs. Deduction limit: ₹10,000.
- 80TTB: Available only for senior citizens. Deduction limit: ₹50,000.
If you’re a senior citizen, Section 80TTB provides a greater benefit.
8. How to Claim Section 80TTA Deduction in ITR
Claiming 80TTA is straightforward:
- Include the interest income under “Income from Other Sources.”
- Deduct up to ₹10,000 under Section 80TTA.
- File using the right ITR form (ITR-1 or ITR-2).
- Submit before the due date.
9. Step-by-Step Process to Report Savings Bank Interest
- Gather Statements: Collect all savings account interest details.
- Calculate Total Interest: Add up the interest from all accounts.
- Declare in ITR: Mention under “Income from Other Sources.”
- Claim Deduction: Apply Section 80TTA up to ₹10,000.
- Submit Return: Double-check and e-file.
10. Benefits of Section 80TTA Deduction
- Reduces Taxable Income → Saves money.
- Encourages Savings → Motivates taxpayers to keep funds in banks.
- Simple Process → No complex paperwork required.
It’s like getting a small umbrella that shields you from a downpour of taxes.
11. Common Mistakes to Avoid While Claiming 80TTA
- Not reporting interest income at all.
- Claiming deduction on FD or RD interest (not allowed).
- Claiming under the new regime (not valid).
Avoid these mistakes to prevent unnecessary scrutiny from the Income Tax Department.
12. Old vs. New Tax Regime: Where Does 80TTA Fit?
- Old Regime: You can claim deductions like 80TTA, 80C, HRA, etc.
- New Regime: Lower tax rates, but no deductions like 80TTA.
If you earn substantial savings interest, the old regime may be more beneficial.
13. Role of Automatic Income Tax Calculator All in One




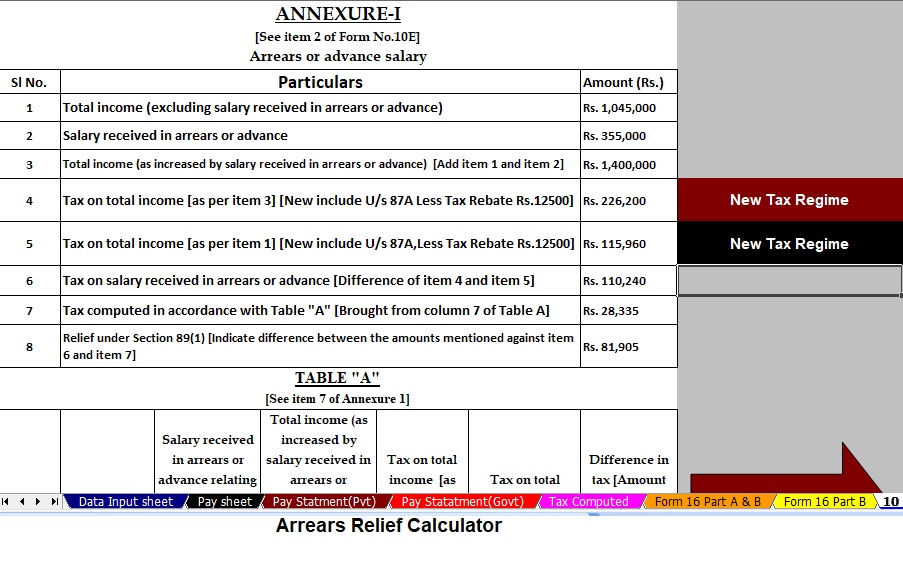
Filing taxes manually can feel like navigating a maze. An Automatic Income Tax Calculator in Excel makes it seamless by:
- Computing tax liability automatically.
- Including pre-built salary structures for Govt & Non-Govt employees.
- Handling deductions and exemptions with ease.
14. Features of the Excel Utility with Form 10E
This tool is a one-stop solution for salaried individuals. It:
- Automatically calculates tax liability.
- Prepares Form 16 (Part A & B).
- Calculates HRA exemption U/s 10(13A).
- Provides arrears relief U/s 89(1) with Form 10E (from F.Y. 2000-01 to F.Y. 2025-26).
- Generates automatic salary sheets.
It’s like having a personal tax assistant—only smarter, faster, and error-free.
15. Conclusion: Maximise Your Savings with 80TTA
Section 80TTA offers a simple yet effective way to save tax on your savings bank interest. By claiming this deduction under the old regime, you can reduce taxable income, encourage savings, and avoid unnecessary tax payments.
Pair this with the Automatic Income Tax Calculator in Excel with Form 10E, and filing becomes stress-free. Whether you’re a Govt or Non-Govt employee, this tool ensures you never miss out on benefits.
FAQs
- Can I claim Section 80TTA deduction under the new tax regime?
No, 80TTA is available only under the old regime. - Is a savings account fully tax-free under 80TTA?
No, only up to ₹10,000 is deductible. Any amount above that is taxable. - Can senior citizens claim 80TTA?
Senior citizens can instead claim Section 80TTB, which allows up to ₹50,000 deduction. - Do I need to submit proof to claim 80TTA?
No proof is required to claim, but you must correctly report interest income in your ITR. - Can I claim 80TTA for multiple savings accounts?
Yes, the deduction applies to the total interest from all savings accounts, capped at ₹10,000.
Download the Automatic Income Tax Preparation Software in Excel – All in One with Form 10E for the Financial Year 2025-26.
The features of this Excel utility include:
-
It automatically calculates your tax liability and prepares the detailed Tax Computed Sheet.
-
It provides an inbuilt salary structure, and therefore, suits both Government and Non-Government employees.
-
It calculates House Rent Allowance (HRA) exemption under Section 10(13A), and as a result, ensures accuracy.
-
It computes Income Tax Arrears Relief under Section 89(1) with Form 10E, covering financial years from 2000-01 to 2025-26.
-
It generates automatic salary sheets for both Government and Non-Government employees, thereby saving time.
-
It prepares Income Tax Form 16 Part B automatically, which simplifies the documentation process.
-
Finally, it creates Income Tax Form 16 Part A and Part B together, and thus, offers complete compliance support.




